Contents
What Is Protein Fasting, and How Does It Work?
Protein fasting or protein cycling is a practice in which you limit your protein intake to approximately 15 to 25 grams for one to three days per week.
Although there isn’t much information or scientific research about this type of fast, its general guidelines suggest eating more healthy fats and carbohydrates like vegetables and fruits instead of protein.
Note: do not confuse protein fasting with a protein-sparing modified fast diet, which is an entirely different approach.
A protein fast is believed to have multiple benefits for your general health, as it:
- Helps prevent chronic diseases in the kidneys
- Increases life expectancy
- Promotes healthier blood sugar metabolism
Take a
1-minute quiz
and discover how much weight you can lose with DoFasting!
Protein Fasting vs. Intermittent Fasting
Protein fasting and intermittent fasting are completely different fasting methods. Still, both are based on the same premise—reducing our daily calorie intake has positive long-term health benefits.
Standalone intermittent fasting is the practice of abstaining from food for a specific period—you don’t eat anything during your fasting window, and then you eat whatever you want during the rest of the day.
Protein fasting differs from a typical fast in that you don’t need to be on an empty stomach if you start feeling the need to eat: you just need to focus on lowering your protein intake and eat healthy fats and carbohydrates freely.
Although they may sound similar, the most significant difference between both fasting methods is the amount of scientific research backing them. While intermittent fasting is proven to be a safe habit with multiple benefits for the body, the science supporting protein fasting is still quite limited.
How Do You Practice Protein Fasting?
Protein fasting has pretty straightforward guidelines:
- Limit your protein intake to 15-25 grams a day for 1-3 days a week
- Eat more nutrient-dense foods, healthy fats, and carbohydrates
- Follow your regular diet on the remaining days with no food limitations
The key to this fasting style is to carefully track the grams of proteins you consume to ensure you’re within the recommended intake, be it with an app, manually, or with an eating plan recommended by your dietitian.
While correctly following a protein cycling diet, your calorie intake should naturally drop, which can help you lose weight and improve your health.
If you want to start protein fasting, make sure to fill up your fridge with foods rich in fiber and healthy carbs:
- Healthy fats — coconut oil, olive oil, bone broth, MCT oil, etc.
- Grains — bread, pasta, oats, rice, etc.
- Fruits — apples, bananas, peaches, berries, lemons, grapefruit, etc.
- Vegetables — sweet potatoes, zucchini, carrots, cucumber, celery, broccoli, leafy greens, etc.
Also, make sure you don’t eat too much protein by avoiding these foods:
- Meats — chicken, turkey, pork, and beef.
- Fish — salmon, tuna, crabs, etc.
- Eggs — chicken and duck eggs.
- Dairy products — milk, cheese, yogurt.
- Soy products — tofu, natto, etc.
- Nuts — almonds, walnuts, pistachios, etc.
- Seeds — chia seeds, hemp seeds, etc.
And a final tip: drink plenty of water, green tea, or lemon juice to stay hydrated and enhance your results. If you need more ideas, take a look at our list of drinks you can enjoy during your fast, which can also be applied to protein cycling.
How Does Protein Fasting Work for Weight Loss?
Low-protein diets are believed to promote long-term weight loss, and the reason for this is the same as with any other fasting style—reducing your protein intake naturally means limiting your overall food intake.
By limiting the proteins you eat, you mimic the effects of intermittent fasting or calorie restriction, boosting your metabolism and helping your body to burn fat.
But while a reduced calorie intake is known to have multiple benefits for your overall health and weight loss, there is minimal evidence that eating fewer proteins has any advantages for healthy adults.
Protein fasting is generally recommended for people with problems in the kidney, severe cirrhosis, or issues related to protein metabolism, as it can actually help in these cases.
How Does Protein Fasting Affect Muscle Mass?
There isn’t a clear answer to how protein fasting affects muscles. Some research suggests that this diet doesn’t interfere with muscle building as it induces autophagy, a process needed to maintain muscle mass.
However, if your body doesn’t receive the required daily amount of protein, it could tear down muscle instead of building it, especially in elderly people. Moreover, low protein intake can negatively affect muscle strength and physical performance in later life.
Protein fasting can also slow down muscle building for healthy adults. Nonetheless, if you eat enough calories and exercise regularly, this diet should not affect your muscle mass.
Basically, whether or not protein fasting can help with building muscle depends on each person, although there is no science-based support to claim this.
Other Important Health Benefits of Protein Fasting
Similarly to intermittent fasting, food-restricting diets have essential health benefits aside from weight loss.
Promotes autophagy
As we mentioned above, protein fasting promotes autophagy. This cellular process recycles cells, removes damaged ones, and destroys viruses and bacteria, fostering better health and longevity in the long run. It’s the body’s natural cleaning process, and it also helps fight chronic diseases.
Autophagy is activated by glucagon, a hormone segregated by the pancreas when there is no glucose for the body to utilize for energy and in response to high levels of amino acids. High levels of glucagon help regulate your blood sugar levels and decrease your appetite.
Controls inflammation
Studies show that low-protein diets such as protein cycling can help reduce concentrations of various inflammatory biomarkers and increase adiponectin, a protein hormone with anti-inflammatory properties.
In addition, protein fasting can reduce methionine levels, probably leading to decreased inflammation and oxidative stress.
Reducing inflammation is important, as it can disrupt your metabolic homeostasis and make it hard for you to lose weight. Inflammation is also associated with cardiovascular and autoimmune diseases, mental illnesses, and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
Avoiding chronic inflammation is crucial for your heart health, immune system, and successful weight loss.
Increases longevity
According to some animal studies, low protein consumption is linked to a longer life expectancy and a lower risk of cancer, heart disease, diabetes, and other chronic diseases.
Having low protein days and a higher intake of vegetables could also decrease the risk of cardiovascular and autoimmune diseases, contributing to longevity.
Take a
1-minute quiz
and discover how much weight you can lose with DoFasting!

Side Effects and Drawbacks to Consider
While this fast is believed to have promising health benefits, it is essential to remember that protein is a crucial nutrient for the human body. So you may want to be aware of the potential side effects of protein deficiency before you try this diet for the first time.
You may feel hungrier than usual
Feeling satisfied with your meal might be directly linked to how much protein you consume. Protein deficiency can leave you feeling unfulfilled even after eating large meals, increasing your hunger levels throughout the day.
Studies have indicated that those who eat less protein are more likely to acquire weight precisely because of the decreased satisfaction associated with lower protein consumption and bad fat-free mass preservation.
Thankfully, this side effect is easy to overcome: plan your meals in advance, eat protein-rich foods on non-fasting days, minimize your protein-fasting days and carry healthy, low-protein snacks with you so you’re ready when hunger strikes.
Certain cravings
Having specific cravings is also associated with a low-protein diet. Specifically, you could feel the urge to eat two kinds of foods:
- You will likely feel more sugar cravings than usual, as you’ll consume more foods high in carbs, which can impact your glucose levels.
- You may also feel protein-rich food cravings, such as wanting to eat meat.
However, there aren’t enough studies on this topic to draw a conclusion. The appearance of these cravings could depend entirely on each individual.
To make sure you avoid this side effect, eat nutritious foods during your protein fasting days and avoid highly processed meals.
Workouts may be more challenging than usual
Since proteins are rich in amino acids, protein fasts might lead to lower oxygen levels and tiredness, making you feel like you’re lacking the energy to reach top performance in your workouts.
While fasting, you could also experience symptoms of edema—the retention of liquids in your body that leads to weight gain and uncomfortable bloating, which could also hinder your workouts.
To alleviate these side effects, stick with low-intensity workouts like walking, cycling, or yoga. Drink enough water, sleep for at least 8 hours a day and reduce your protein fasting days if needed.
You might feel colder than usual
A rich diet full of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates is essential for thermoregulation in the body. Therefore, deficiencies derived from a reduced protein intake can make you feel colder than usual.
In addition, while protein fasting you naturally consume less food, activating your digestive system less often than you’re used to. Digestion pumps blood around your body, which helps you warm up, so eating less often could lead to cold sensations.
Overall, feeling cold while fasting is normal. If you experience this side effect, make yourself a warm cup of coffee or tea, eat a hot meal, or take a bath to warm yourself up.
Other health issues
A protein deficiency can cause multiple health issues:
- Thinning hair and nails
- Immune system impairment
- Slow healing of wounds
- Weakness and loss of muscle mass
If you feel any of the above, stop your fast and consult your doctor for the best course of action.
3 Tips to Make Protein Fasting Work for You
If you feel like giving this diet a go, here are a few tips to make the protein fast easier to stick with:
1. Track your protein intake
To make sure you’re sticking to your daily 15 to 25 grams of protein, it is crucial that track your food intake.
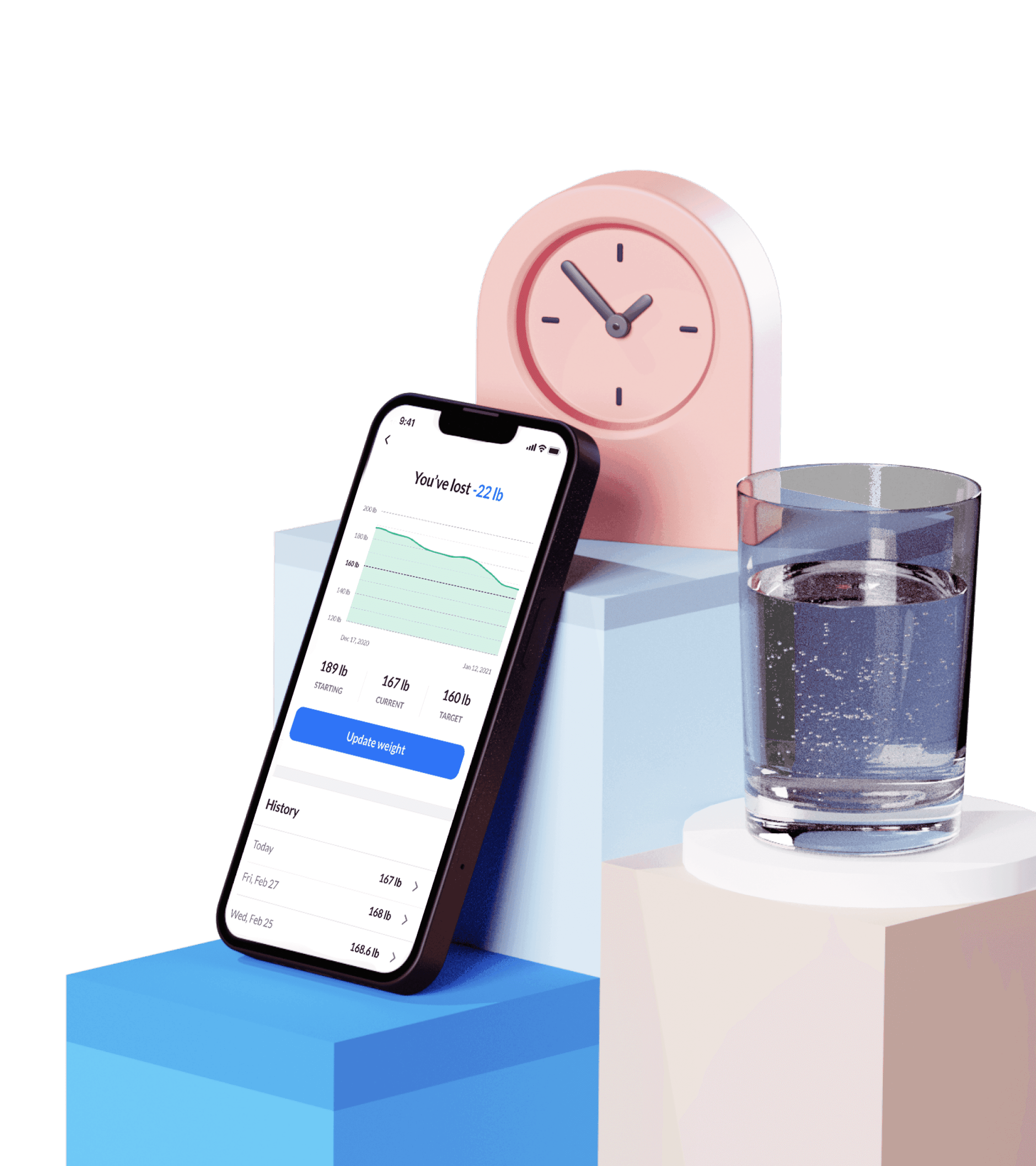
You can get a dietitian to make you a meal plan, or you could download an app like the DoFasting app: its calorie and meal tracking feature will help you keep a log of your daily food, so you’ll have full control over your progress and your goals.
2. Use a digital scale in your kitchen
A kitchen scale doesn’t take up a lot of space in your kitchen, and it can be a really helpful tool to have: you’ll be able to measure your portions of protein-rich foods to make sure that you are not breaking your protein fast, and it will help you plan your meals according to your weight loss plans.
3. Have low-protein foods in your refrigerator
The goal of this diet is to naturally lower your protein consumption by replacing protein-packed foods with veggies and grains, so it is essential to fill up your pantry with these food groups before your first fast.
Keeping the right kinds of foods at hand will help you stay on track and resists any potential cravings for sugar, protein, or processed foods.
Some examples of low-protein foods that you could gather before starting this new habit include:
- All fruits
- All vegetables except peas, beans, and corn
- Healthy such as olive oil and avocados
- Bread
- Rice
- Oats
- Pasta
Make sure to have low-protein food variations in your kitchen at all times, and plan your meal ideas and snacks to resist cravings.
Take a
1-minute quiz
and discover how much weight you can lose with DoFasting!

Protein Fasting: Key Takeaways
Protein fasting or protein cycling is a diet that restricts your protein consumption to 15 to 25 grams for one to three days a week.
This eating habit is believed to have multiple benefits, including promoting autophagy, inflammation control, and increased longevity. However, it is hard to stick with, and there is little scientific evidence backing these claims.
If you’re looking for a new eating habit that can help you lose weight and enjoy multiple health benefits, there are plenty of alternatives available such as the keto diet (a low-carb diet) or the most popular kind of fasting—intermittent fasting.
See how DoFasting will improve your life
Find out what works for you with this 60-sec quiz approved by our experts and get your personal revolutionary fasting assistant.
Start the Quiz